
How to Become a SOC Analyst?
- Posted by 3.0 University
- Categories Cyber Security
- Date May 2, 2025
- Comments 0 comment
The Role of a SOC Analyst
Companies today battle an ongoing digital storm—a fast-changing scene filled with cyber troubles that force them to be ever-watchful and quick on the draw.
SOC analysts, the cybersecurity pros working inside Security Operations Centers, really come to the forefront here.
They’re busy scanning security alerts, digging into incidents, and stepping up when something seems off, all to keep sensitive data safe and operations running smoothly.
Their collaborations is often with IT, executive teams and even legal, all through intense and sometimes nerve-wracking crises.
The statement, “SOC analysts are normally part of a large, dedicated team that acts as the last line of defense against cybercrime,” precisely recapitulates their decisive role in recognizing and thwarting threats before any serious damage ensues.
All things considered, getting a sense for what SOC analysts do really cliques the stage for comprehending the combination of specialized skills and hard-earned training needed to thrive in this challenging yet rewarding field of cybersecurity.
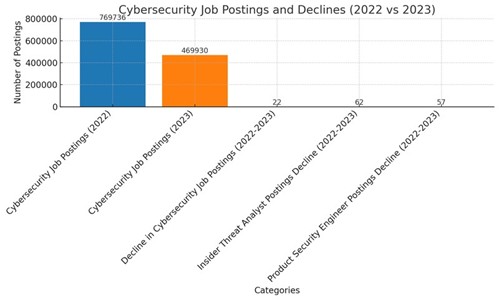
The bar chart shown above demonstrates the extensive decline in cybersecurity job postings in the U.S. from 2022 to 2023 – highlighting the drop in overall job postings apart from specific positions viz. Insider Threat Analysts and Product Security Engineers, reflecting the challenges facing the cybersecurity workforce.
SOC Analyst Responsibilities
The dynamism of the Cybersecurity field is exemplary and pivotal where threats continually proliferate and evolve, necessitating professionals to stay vigilant at all times.
Most of the people here tend to be in a constant clamber against dangers that morph unexpectedly.
At the centre of this hustle is the SOC Analyst. They don’t just sit back and watch automated alerts from advanced SIEM tools; instead, they dive in to spot even the faintest signs of trouble and act fast before issues balloon.
Occasionally, it’s about their proactive approach involves identifying subtle signs of compromise that routine systems might miss.
the hard work of digging into logs, unravelling incident details, and keeping meticulous records (which, in most cases, help with compliance and ongoing tweaks to security measures).
Collaboration is key, too—working hand-in-hand with IT, legal, and executive folks to set up solid strategies that manage and mitigate incidents.
They master a wide variety of skills, from understanding networking protocols to wrestling with firewalls and intrusion detection systems, all while piecing together complex data and making crucial calls under pressure.
The career hierarchy illustrated in the table shows just how foundational the SOC analyst’s role is—and hints at how responsibilities can evolve and open up new avenues in this high-stakes realm. Let’s also dive into SOC analyst job descriptions.
Responsibility | Description |
Monitoring and Detection | Continuously monitor networks, systems, and applications using tools like SIEM to detect unusual or suspicious activities indicating potential security incidents. |
Incident Response | Swiftly respond to detected incidents by investigating alerts, analyzing the nature and scope of threats, and containing and mitigating their impact to prevent further damage. |
Threat Hunting | Proactively search for signs of advanced threats that may evade traditional security measures by analyzing logs, network traffic, and other data sources to detect anomalies or patterns indicative of malicious activity. |
Vulnerability Management | Conduct vulnerability assessments and prioritize remediation efforts to mitigate security risks, ensuring timely application of patches and updates. |
Forensics and Investigation | Perform detailed forensic analysis of security incidents to determine impact and recovery strategies, documenting findings and lessons learned. |
Security Awareness and Training | Promote cybersecurity awareness across the organization by developing and delivering training programs to educate employees on best practices and incident response procedures. |
Compliance Monitoring | Ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards by supporting compliance audits and providing necessary documentation. |
Continuous Improvement | Collaborate with other cybersecurity teams to improve security tools, processes, and procedures, participating in exercises and simulations to test incident response plans. |
Key Responsibilities of a SOC Analyst
Essential SOC Analyst Skills
It one’s aim is to work as a SOC analyst, then the person verily needs to be, invariably, both solid tech smarts and a knack for analysing stuff.
Being cognizant of their way around basics like TCP/IP and DNS—and being comfortable with systems such as Windows and Linux—lets you jump between different IT setups without too much fuss.
For effective monitoring crucial threats in real-time, the adroitness to manage SIEM tools such as Splunk or IBM QRadar is extremely essential and paramount. Simultaneously, one has to piece together a jumble of data clues to catch any oddities that could point to a security breach.
Being up on incident response ideas like the MITRE ATT&CK model usually sets you up to handle cyber risks faster.
Moreover, having the ability to communicate clearly and make quick decisions under pressure is crucial when collaborating with IT teams, legal professionals, and executives during a crisis.
In most cases, mixing all these skills boosts a company’s cyber defence, aligning with the structured career progression depicted in the table.
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | Skill ID | Skill Name |
Security Control Assessment | Data Analysis | Multi-Disciplined Language Analysis | Cyberspace Operations | S0710 | Evaluating Metadata |
Cyber Defense Analyst | 19 | Knowledge of cyber defense and vulnerability assessment tools | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 22 | Knowledge of computer networking concepts and protocols, and network security methodologies | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 59A | Knowledge of Intrusion Detection System (IDS)/Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) tools and applications | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 66 | Knowledge of intrusion detection methodologies and techniques | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 70 | Knowledge of IT security principles and methods | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 81A | Knowledge of network protocols such as TCP/IP, DHCP, DNS, and directory services | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 87 | Knowledge of network traffic analysis methods | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 92 | Knowledge of how traffic flows across the network | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 108 | Knowledge of risk management processes | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 150 | Knowledge of what constitutes a network attack and the relationship to both threats and vulnerabilities | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 214A | Skill in performing packet-level analysis | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 353 | Skill in collecting data from a variety of cyber defense resources | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 433 | Characterize and analyze network traffic to identify anomalous activity and potential threats | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 472 | Coordinate with enterprise-wide cyber defense staff to validate network alerts | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 723 | Document and escalate incidents that may cause ongoing and immediate impact | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 745 | Perform cyber defense trend analysis and reporting | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 750 | Perform event correlation using information gathered from various sources | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 767 | Perform security reviews and identify security gaps in security architecture | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 800 | Provide daily summary reports of network events and activity relevant to cyber defense practices | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 823 | Receive and analyze network alerts from various sources and determine possible causes | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 895 | Skill in recognizing and categorizing types of vulnerabilities and associated attacks | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 922B | Skill in using network analysis tools to identify vulnerabilities | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 956 | Provide timely detection, identification, and alerting of possible attacks/intrusions | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 958 | Use cyber defense tools for continual monitoring and analysis of system activity | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 959 | Analyze identified malicious activity to determine weaknesses exploited | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 984 | Knowledge of cyber defense policies, procedures, and regulations | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 990 | Knowledge of the common attack vectors on the network layer | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 991 | Knowledge of different classes of attacks | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 1069A | Knowledge of general kill chain | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 1107 | Identify and analyze anomalies in network traffic using metadata | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 1108 | Conduct research, analysis, and correlation across a wide variety of all source data sets | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | 1111 | Identify applications and operating systems of a network device based on network traffic | |||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 1157 | Knowledge of national and international laws, regulations, policies, and ethics as they relate to cybersecurity | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 1158 | Knowledge of cybersecurity principles | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 1159 | Knowledge of cyber threats and vulnerabilities | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 6900 | Knowledge of specific operational impacts of cybersecurity lapses | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 6935 | Knowledge of cloud computing service models | ||
Cyber Defense Analyst | Vulnerability Assessment Analyst | 6938 | Knowledge of cloud computing deployment models |
Essential Skills Required for SOC Analyst
SOC Analyst Career Path and Progression
Career progression in a Security Operations Center (SOC) more than mere a neat ladder to ascend —it’s more like a zigzagging path wherein every twist or turn demands more responsibility and hands-on know-how.
Most of their career commences as Tier 1 analysts, tasked with monitoring alerts and managing basic incident triage; this stage focuses on mastering threat detection techniques and determining when to raise issues.
Moving on to Tier 2, professionals begin digging into deeper investigations—engaging in threat hunting and forensic analysis that gradually sharpens their ability to spot intricate attack routes and hidden vulnerabilities.
At the Tier 3 level, things shift; experienced analysts take charge by managing escalations, steering response efforts, and even getting involved in red teaming exercises that, in most cases, play a pivotal role in shaping an organization’s overall security stance.
Beyond these levels, the career journey might veer into roles like Incident Response Manager, SOC Manager, Security Architect, or even Cybersecurity Consultant—each needing a broader strategic vision mixed with solid leadership skills.
Overall, this layered framework—detailed, generally speaking—underscores the multifaceted nature of SOC careers, where ongoing skill-building and key certifications can really help push you upward.
Here’s a tiny but gratifying data of SOC analyst salary…
Experience Level | Median Salary (USD) | Top 10% Salary (USD) | Bottom 10% Salary (USD) | Sample Size | Year |
Entry-level / Junior | 82000 | 155000 | 51000 | 240 | 2024 |
Mid-level / Intermediate | 81000 | 155000 | 51000 | 240 | 2024 |
Senior-level / Expert | 129956 | 183300 | 95000 | 34 | 2024 |
SOC Analyst Career Progression and Salary Data
Conclusion
A well-developed career in cybersecurity apart from necessitates inquisitive and flexible mindset that allows for quick learning apart from extraordinary technical skills.
It one is planning for a future as an SOC Analyst, he/she really needs to cobble together an extensive array of skills, right from being mindful of their way around networking protocols and SIEM tools to having that keen, almost instinctive analytical edge and the knack for clear, direct communication.
Real-world SOC analyst training sessions—plus those industry-respected certifications—often mark important milestones that not show you’ve got the know-how and boost appeal in the job market.
Furthermore, comprehending the typical progression of careers in security operations enables you to strategize for the long term, whether your goal is to advance as a senior analyst or venture into areas such as threat intelligence or incident response.
SOC analyst certification, apart from an excellent combination of ongoing learning, solid technical insight, and a little deftness of career mapping lands SOC Analysts squarely on the cyber defence frontlines, wherein it’s immensely essential for them to stay on their toes as threats evolve.
This engagement in such a dynamic field offers them the opportunity to play a vital role in safeguarding our digital world beyond merely providing professional satisfaction.
Most certainly, it befalls as an amply challenging, and sometimes, equally unpredictable journey—a path that’s as gratifying as it is dynamic and crucial in keeping our digital assets safe.
Empower your career with 3.0 University next-gen online courses in Web3 technologies. Explore the AI-Powered Ethical Hacking Program, dive into advanced cybersecurity, and master Blockchain and AI innovations—all with global certifications.
You may also like

How to protect seniors from online scams?

When AI Hacks Back: Cybersecurity in 2025

